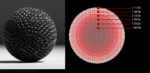
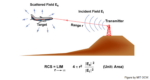
The Luneburg lens is an extremely efficient reflector of radar energy based on advanced principles and fabrication techniques. The theoretical Luneburg lens requires a smooth, continuous gradient of the refractive index from the center to the outside. In practice, this is generally not a viable type of construction (but that is changing). Q: What is […]
FAQ
FAQ on Luneburg lens to increase radar signature part 2
The Luneburg lens is an extremely efficient reflector of radar energy based on advanced principles and fabrication techniques. This section looks at the Luneburg lens, used to enhance radar visibility by increasing the RCS. Q: What is a Luneburg lens? A: There are several ways to describe it, both qualitatively and quantitatively. The Luneburg lens […]
FAQ on Luneburg lens to increase radar signature: Part 1
The Luneburg lens is an extremely efficient reflector of radar energy based on advanced principles and fabrication techniques. You’re undoubtedly familiar with the concept of radar, radar reflections, and the importance of minimizing reflecting in order to be less visible to a radar beam. As radar technology advanced through various improvements such as use of […]
If you are working with power management here are some tools to consider, part 2
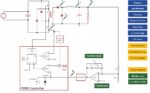
Power management encompasses a range of power converter types and topologies and includes systems like motor drives, ac/dc power supplies, dc/dc converters, and battery chargers. Designing compact, cost-effective, and efficient power management systems is challenging and requires a combination of skills in high voltage and high current design, control loop optimization, mitigation of electromagnetic interference […]
If you are working with power management here are some tools to consider, part 1
Power management encompasses a range of power converter types and topologies and includes systems like ac/dc power supplies, dc/dc converters, LED lighting, and battery chargers. Designing compact, cost-effective, and efficient power management systems is challenging and requires a combination of skills in high voltage and high current design, control loop optimization, mitigation of electromagnetic interference […]
If you are working with video signal processing here are some tools to consider, part 2
Computer and machine vision based on video signal processing and analysis is a critical function in systems like autonomous vehicles, medical imaging diagnostic equipment, facial recognition and eye tracking applications, smart cities, supply chain management, and robotics. It requires rapid and accurate object and feature recognition and extraction. Implementation of computer vision is complex and […]
If you are working with video signal processing here are some tools to consider, part 1
Computer and machine vision based on video signal processing and analysis is a critical function in systems like autonomous vehicles, medical imaging diagnostic equipment, facial recognition and eye tracking applications, smart cities, supply chain management, and robotics. It requires rapid and accurate object and feature recognition and extraction. Implementation of computer vision is complex and […]
If you are working with antennas, here are some tools to consider, Part 2
Antenna design and integration is an important activity for 5G telephony, wireless Internet of Things (IoT) nodes, Wi-Fi networks, near field and satellite communications, and a range of other applications. Without robust antenna designs and solid system integration, the performance of those applications can be severely compromised. Balancing the needs for efficiency, gain, bandwidth, pattern […]
If you are working with antennas, here are some tools to consider, Part 1
Antenna design and integration is an important activity for 5G telephony, wireless Internet of Things (IoT) nodes, Wi-Fi networks, near-field, and satellite communications, and various other applications. Without robust antenna designs and solid system integration, the performance of those applications can be severely compromised. Balancing the needs for efficiency, gain, bandwidth, pattern characteristics, and decreased […]
The Radio Data System: FM radio adds features to stay viable, part 4
Broadcast FM radio has extended its user-friendly capabilities through the addition of embedded, backward-compatible functionality which adds text and even graphics to the radio display. This part concludes with additional RDS details and IC implementations. Q: Where is the RDS signal in the FM-channel spectrum? Does it affect existing FM stereo broadcasts? A: One of […]