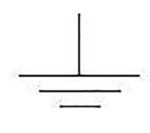
The term “ground” is one of the most frequently used words in electronics, and it’s also one of its most-often misused and misunderstood terms. Fortunately, in many cases of misuse, the engineers using it know what it actually being referred to, and are able to translate it internally and so avoid negative consequences. However, there […]
FAQ
What are some specialized op amp variations?
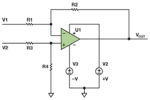
The operation amplifier – commonly called the op amp – is the key building block of analog circuits. In its basic configuration, it is most often used to amplify a signal, of course. It can also be configured to perform mathematical operations such as implementing multiplication or division of two signals, take a square root, […]
Working with op amps: tying down floating pins
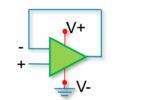
Operational amplifiers are used in many configurations and with many variations on specifications, depending upon the application. However, an IC package of operational amplifiers will often come with several in a package (e.g., a “quad pack” will have four op amps). If you have leftover, unused op amps on the same chip, the unused ones […]
Electrostatic discharge and analog circuits: Preventing the undetectable disaster
Analog circuits are exposed to outside influences most often through input channels by way of op amps acting as filters, buffers, or amplifiers. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) results from the direct contact of two things that are at different voltage potential levels and can also be defined as a fast, high current transfer. Analog circuit exposure […]
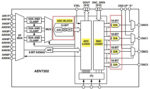
What is a CODEC?
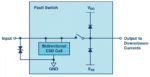
In the embedded hardware world, the term CODEC stands for COder/DECoder and is basically an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) in one package. A codec, whether hardware or emulated in software, converts analog audio signals into digital signals for transmission or encodes them for storage in a digital format. Later, the decoder […]
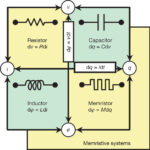
Memristors, the fourth fundamental circuit element
Professor Leon Chua of the Electrical Engineering Department of UC Berkeley coined the term memristor while working on mathematical models in electrical engineering. He noted that resistors relate voltage to current (R=V/I), capacitors relate charge to voltage (C = Q/V), and inductors relate magnetic flux to current (L= Φ/I). What seemed to be missing was a […]
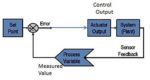
What is Proportional (PID) Control and why is it used? (Part 2)
Part 1 of this FAQ looked at the strengths and weaknesses of basic on/off control as well as the performance improvements that the proportional, integral, and derivative (PID) control algorithm provides. PID analysis PID performance and its setup has been the subject of countless articles, Ph.D. dissertations, tutorials, books, and courses which span qualitative, mostly […]
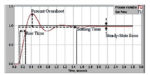
What is Proportional (PID) Control and why is it used? (Part 1)
Closed-loop control is the foundation of our modern automated world. In simplest terms, this approach applies negative feedback to a system to achieve a desired result. Consider the control of temperature, the most widely measured and controlled real-world physical parameter. If the measured value of this process variable is above the desired setpoint value, we […]
Digital potentiometer or digipot: applications and uses
A digital potentiometer (or “digipot”) operates like a traditional mechanical potentiometer (pot), which is a variable resistor, except the digipot is an integrated chip (IC) that accepts signal input rather than the physical movement of a shaft or slide for adjustment. Essentially, both types of potentiometer are analog devices that provide variable resistance. However, a […]
RTD vs. thermocouple vs. thermistor in temperature sensors
Temperature doesn’t change very quickly, and temperature sensors match that characteristic. Environmental temperature changes are generally slow, on the order of less than 0.1 sec/°C. Typical temperature sensors used in circuits are resistance temperature devices (RTDs), thermocouples, thermistors or integrated silicon sensors. Trade-offs amongst these devices include cost, cost to operate, response time, noise immunity, […]