Opportunities for electrically-propelled autonomous mobility and advanced automation continue to multiply in the quest for greater industrial productivity, smarter living, and increased energy efficiency. Encoders can play a large part in these applications as motors require precisely tracked position and motion. However, with multiple encoder types and communication protocols on the market, what are the various options, and which offer the most benefits based on different design requirements?
Opportunities for electrically-propelled autonomous mobility and advanced automation continue to multiply in the quest for greater industrial productivity, smarter living, and increased energy efficiency. Encoders can play a large part in these applications as motors require precisely tracked position and motion. However, with multiple encoder types and communication protocols on the market, what are the various options, and which offer the most benefits based on different design requirements?
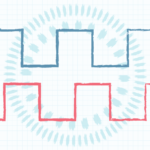
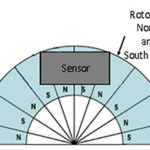
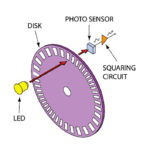
Depending on the application, a controller or variable-speed electric-motor drive may need to measure any combination of rotor speed, position, and direction. A rotary encoder is the go-to device for this purpose and can be either an incremental type that gives position relative to a reference point or an absolute encoder that expresses a unique code for each rotor position.
Although both types operate along similar principles, the absolute encoder is able to determine the rotor position as soon as the system is switched on without being initialized and can keep track of the position in the event of unexpected power loss.
Learn more about the benefits and trade-offs of SPI, RS-485, and SSi communications protocols in order to choose the best option for connecting an absolute encoder to a host system from Jason Kelly’s overview in the latest CUI Devices CUI Insights’ blog.