The terahertz part of the electromagnetic spectrum between millimeter waves and optical range remains a largely untapped, difficult-to-use resource; researchers are investigating different techniques for efficiently generating terahertz waves to promote the use of this part of the spectrum.
Approach #1: Lasers and Acoustic Modulation
A recent project and paper by a collaborative team from the University of Leeds and the University of Nottingham (both in the UK) not only provided insight on the generation of terahertz waves but also demonstrated how they employed acoustic, non-EM wave energy to modulate those waves. In a greatly simplified form, what happens is this (Figure 1): A an electron passes through the optical component of the quantum cascade laser, and in doing so, it goes through a series of quantum wells. At these wells, the energy level of the electron decreases, and a photon pulse is emitted, with one electron capable of causing the emission of multiple photons as a steady, continuous-wave (CW) stream.
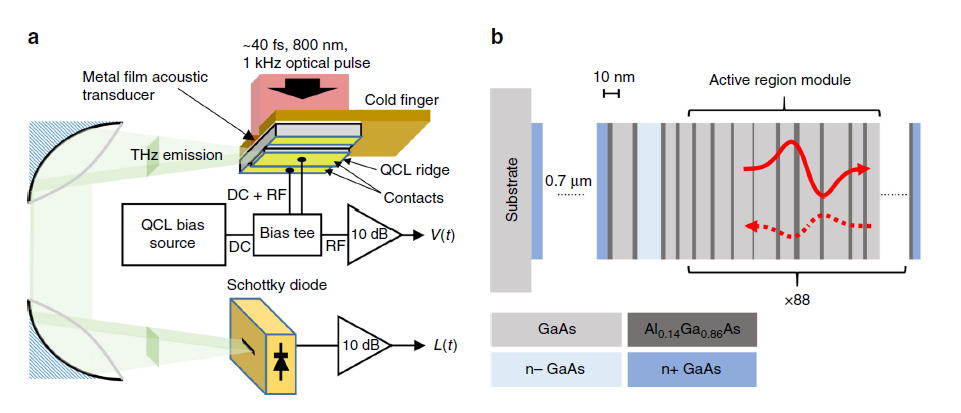
To implement modulation, they focused acoustic-wave energy to vibrate the quantum wells inside the quantum cascade laser. Here, “acoustic wave energy” does not mean they pointed a loudspeaker at the laser source. Instead, they generated the acoustic waves using the impact of a pulse from another laser to induce an optically generated, picosecond-wide, strain pulse on an aluminum-film acoustic transducer. This, in turn, caused that film to expand and contract, thus sending a mechanical wave through the quantum cascade laser, and this wave established the modulation.
Note that the maximum modulation depth they achieved was relatively low, around 6%. That’s a long way from the tens of percent of modulation depth needed for a viable communications link, but it’s a start
Their readable paper, “High-speed modulation of a terahertz quantumcascade laser by coherent acoustic phonon pulses,” was published in Nature Communications (the pdf version is here). The HTML version also has a link to Supplementary Information with extra details on the configuration, BOM, materials used and their preparations, issues faced and overcome details of the test arrangement, and more.
Terahertz Perspectives
IEEE Spectrum, “Wireless Industry’s Newest Gambit: Terahertz Communication Bands”
IEEE Spectrum, “Terahertz Waves Could Push 5G to 6G”
IEEE Spectrum, “The Truth About Terahertz”
EE World Online References
Terahertz Laser Pulses Amplify Optical Phonons in Solids
Terahertz Technology Creates New Insight Into How Semiconductor Lasers Work
Scientists Fine-Tune Carbon Nanotubes For Flexible, Fingertip-Wearable Terahertz Imagers
The Future Of Wireless Communications Is Terahertz
Bridging The Terahertz Gap
Inspecting Matter Using Terahertz Light
Graphene And Terahertz Waves Could Lead The Way To Future Communication
Wave of the Future: Terahertz Chips a New Way of Seeing Through Matter
Terahertz Wireless Could Make Spaceborne Satellite Links as Fast as Fiber-Optic LinksNUS Engineers Develop Low-Cost, Flexible Terahertz Radiation Source for Fast, Non-Invasive Screening
Researchers Whip Up Terahertz Radiation at Room Temperature
Light-powered 3-D Printer Creates Terahertz Lens