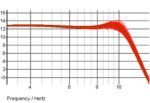
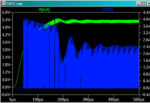
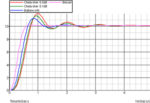
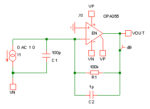
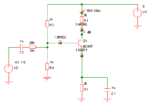
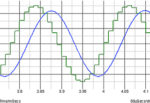
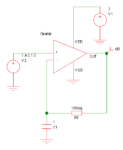
I thought I would share some of the crimes against filters that I have seen people commit over the years. 2+2=4? So, you have designed a 2 pole Butterworth filter for example and want a 4 pole one so you put two of them together. You have a four pole filter? Yes, but not a […]
basics
Using LTspice for power supply design
Simulation using a SPICE simulator (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis) is handy for checking out designs before building them as well as helping to understand designs and circuit problems. You can experiment without blowing anything up! LTspice from Linear Technology is particularly useful as it is free and available to download from their web […]
Analog filters
Filters are an important part of analog design. Even circuits that you don’t think of as filters are actually filters. For example, a simple amplifier will have a bandwidth and so above its upper 3dB point it is a low pass filter. Whole books have been written on filters and filter design, both analog and […]
Transimpedance amplifier signal-to-noise
The use of opamps as a transimpedance amplifier is well known and a good analysis of the noise behavior of them is in the old Burr Brown Application Bulletin AB-076 from 1994. This is still available from Texas Instruments’ web site as sboa060 – simply search for that on their website. Improving the signal to […]
What is a cascode amplifier?
I am not sure how “fashionable” discrete transistor design is nowadays, but anyone using discrete transistors, bipolar or otherwise, for high speed designs other than for switching probably knows about cascode designs. The purpose of a cascode amplifier (not to be confused with cascade which is a chain of two or more amplifiers) is to […]
5 ways to generate a sine wave
It is not uncommon to need a sine wave but how do you generate it? The “best” or most appropriate method for a particular application depends on several things such as: frequency, purity required, amplitude, possible synchronization with another frequency, variable frequency and/or amplitude. At lower frequencies a Wien bridge might be considered – for […]
Open loop gain: how to measure with SPICE
When designing opamps in analog IC design, it is frequently required to plot the open loop gain/phase. One way of doing that is to use a high feedback resistor and very high capacitance so the feedback network has an extremely low corner frequency: This works fine unless your opamp drive capability is low, in which […]