Cables, connectors, and interconnects (cable assemblies) are essential yet often underappreciated parts of a system design. Even though the popular meme is “everything is going wireless” thus eliminating the need for cable assemblies, the reality is that these assemblies are critical both within circuits at either end of a wireless link or as the only […]
basics
RF power measurement, Part 2: What and how
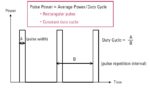
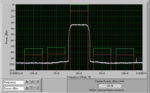
Part 1 of this FAQ introduced some of the basic issues related to the measurement of RF power, which is a primary parameter in most RF designs. Part 2 continues the discussion, looking at RF waveforms and sensors. Q: The term “power” is fairly broad; what are the specifics? A: There are actually several basic […]
RF power measurement, Part 1: Why and where
When the subject is RF design, the word “power” dominates much of the discussion. This FAQ looks at some perspectives related to the measurement of this vital RF parameter. Not only is power and measuring it among the most important RF design considerations, but it is also generally difficult to assess accurately, and it is […]
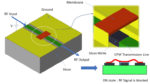
Capacitive RF MEMS switch design and simulation
By Anil Pandey, EDAboard.com member The switching is required in many applications at low as well as at high frequency. RF MEMS switches are the specific micromechanical switches that are designed to operate at RF to mmWave frequencies. MEMS switches usages some mechanical movement to achieve a closed or open circuit in the Radio Frequency […]
The RF power amplifier, Part 2: considerations
Part 1 of this FAQ looked at the basic role and function of the RF power amplifier (PA). This part looks at some of the factors to consider when looking at possible PA devices. It is not a detailed run-through of the many parameters which characterize PAs, including many which are unique to the PA […]
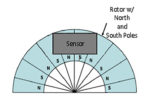
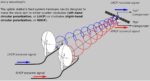
Rotary encoders, Part 2: magnetic encoders
Part 1 of this FAQ looked at the optical rotary encoder, a low-cost, high-resolution, easy-to-use sensor for indicating incremental shaft position (although it can be “upgraded” to indicate absolute position as well). Q: What is the basic principle of the magnetic encoder? A: The magnetic encoder uses a rotating gear made of ferrous metal and […]
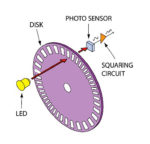
Rotary encoder basics and applications, Part 1: Optical encoders
Across a wide range of applications, it is necessary to need to accurately sense the motion of a rotary shaft and know its position, speed, or even acceleration. To do this, a component called a shaft or rotary encoder is added to the motor/shaft assembly. (Note that the term “rotary encoder” is often shortened to […]
Signal-channel diversity and fading, Part 2: Frequency Diversity
In Part 1 we looked at space diversity, which is the simplest form of signal-channel diversity. It has been used with success since the earliest days of wires and wired links, and it sees new uses in 5G MIMO and other advanced RF systems. We next look at the other very common form of signal-channel […]
Radio receiver architectures, Part 2—Zero-IF and SDR
Part 1 of this FAQ looked at two basic receiver architectures: the tuned radio frequency approach (now largely obsolete due to performance shortcomings), and the superhet design which has been used with great success for about 100 years. Part 2 looks at two other architectures – the zero-IF design and the software-defined radio – which […]
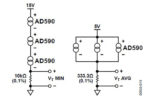
Solid-state temperature sensing, part 2: application
In Part 1, we looked at the basic principle and function of the solid-state temperature sensors, as well as the first widely available model, the AD590. Part 2 looks at some application considerations. Q: What are the interface considerations? A: A basic solid-state sensor has a PTAT current-only output. This means that the subsequent circuitry, […]