Performing these three steps can improve mmWave and beamforming performance.
Size, weight, power, and heat affect 5G base station designs
Engineers designing 5G base stations must contend with energy use, weight, size, and heat, which impact design decisions.
The challenges of building a 5G base station
To meet 3GPP specifications, a 5G New Radio (NR) implementation must meet demanding processing requirements and RF capabilities. Compared to LTE, this results in a need for higher performing, more flexible 5G NR hardware. Looking at 5G’s technical challenges, we see the frequencies and spectrum supported now include a sub-6 GHz range, FR1, with bandwidths…
Why 5G needs over-the-air testing
Over-the-air testing requires different antenna setups for 5G FR1 and FR2. Temperature is a significant factor in calibration and validation.
5 tips for designing with embedded antennas
Designing an antenna into a wireless embedded or IoT device requires special care to maximize performance.
IoT: How 5G differs from LTE
5G extends its scope beyond consumer only to many new vertical and enterprise markets. Thanks to its flexibility and improved performance, 5G opens the door to many industrial applications. When researchers and engineers began developing 5G in 2012, they began to look at use cases. The primary motivation for launching a new generation of wireless…
How to improve 5G coverage and capacity
The laws of physics work against RF engineers, forcing design tradeoffs in mmWave systems. Beam steering, frequency reuse, and greater spectral efficiency can help.
5G radios increase emphasis on compliance testing
Compared to 4G and previous generations, 5G’s mmWave frequencies and tight integration increase the complexity of both performance and regulator compliance testing.
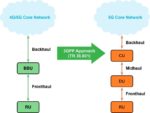
Open RAN functional splits, explained
Open radio access networks offer the option of placing network functions in different places along the signal path. That option, called a functional split, lets network engineers optimize performance and make tradeoffs.