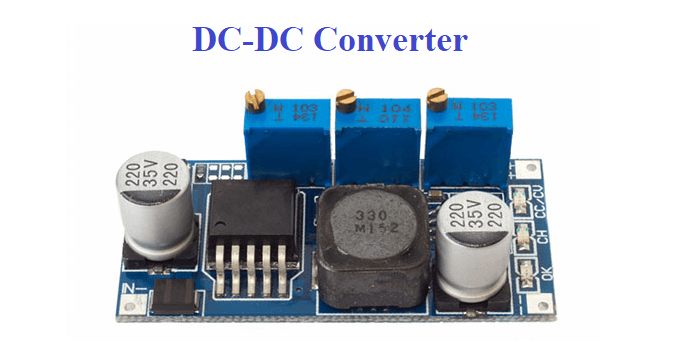
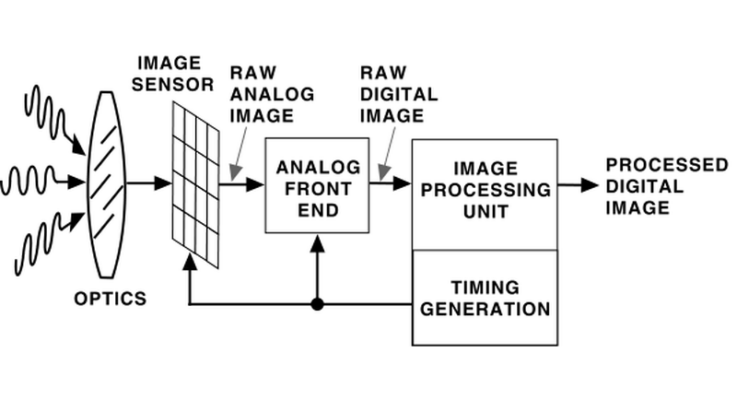
Most electronic systems rely on regulators to deliver stable direct current (DC) levels. This article explains how regulators operate and reviews the … [Read More...] about Why use a switching regulator instead of a linear regulator for DC-to-DC conversion?
Main Content
FAQs

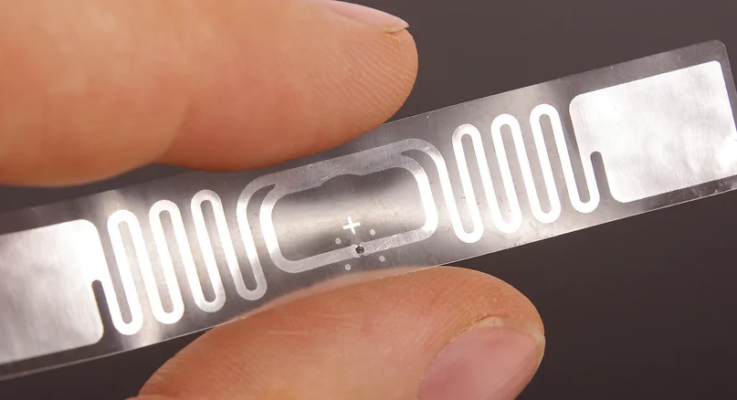
Passive RFID finds unanticipated mass-market applications: part 2
Passive RFID tags have been widely adopted, and some applications show creative adaptation to unmet needs. While many uses for passive RFID tags … [Read More...] about Passive RFID finds unanticipated mass-market applications: part 2
Today on Analog IC Tips
- Compact analog front-end provides efficient electrochemical sensing for next-gen devices
- SIM card level translator boasts ESD protection
- April 2024 Issue: Internet of Things Handbook
- ML algorithms, battery-efficient dashcam kit address parked vehicle monitoring
- Analog and digital capabilities integrated into low-power transceiver
- Why use a switching regulator instead of a linear regulator for DC-to-DC conversion?
- EMI filters protect circuits in space
More Analog IC Product News

Design and simulation powerhouses merge to deliver “silicon-to-systems” approach
Synopsys, a semiconductor design technology company, has announced its acquisition of Ansys, a simulation and analysis solutions provider. The deal, valued at approximately $35 billion, is expected to … [Read More...] about Design and simulation powerhouses merge to deliver “silicon-to-systems” approach
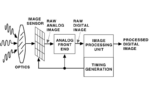
What is analog design for integrated circuits?
Analog design for integrated circuits (ICs) involves creating devices and systems that process continuous signals. Analog plays a crucial role in translating real-world information such as sound, … [Read More...] about What is analog design for integrated circuits?

If you’re designing mixed-signal ICs, here are some tools to consider
Mixed-signal ICs are increasingly common in automotive, internet of Things (IoT), medical, industrial, consumer, and other applications. Designing mixed-signal ICs is more complex than simply … [Read More...] about If you’re designing mixed-signal ICs, here are some tools to consider
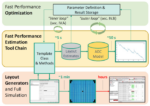
What are the elements of analog IC EDA tools?
Analog functions like sensor interfaces, signal conditioning, power management, and energy harvesting are needed in many applications. These functions are implemented with circuits like operational … [Read More...] about What are the elements of analog IC EDA tools?
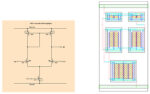
If you’re designing analog ICs, here are some tools to consider
Designing analog ICs can be a time-consuming and nit-picky process. As with the design of digital ICs, speed, power, and area (SPA) considerations are important. However, in the case of analog ICs, … [Read More...] about If you’re designing analog ICs, here are some tools to consider

Managing design complexity and global collaboration with IP-centric design
Semiconductor design complexity has increased exponentially in recent years, and this challenge is exacerbated by the need to collaborate and scale across multiple, globally distributed teams while … [Read More...] about Managing design complexity and global collaboration with IP-centric design

4-port, GbE PHY includes SAR ADC
Faraday Technology Corporation announces the availability of its 4-port Gigabit Ethernet PHY on UMC's 28HPC+ process. This silicon-proven GPHY features an SAR ADC for superior PPA advantages and an … [Read More...] about 4-port, GbE PHY includes SAR ADC

Siemens expands capabilities of IC design tools with EDA acquisition
Siemens Digital Industries Software announced that it has completed the acquisition of Insight EDA Inc., an EDA software company delivering groundbreaking circuit reliability solutions to many of the … [Read More...] about Siemens expands capabilities of IC design tools with EDA acquisition
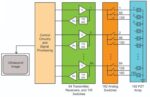
How to specify and use analog switches
An analog switch is an IC that can be used to control connections to analog and digital signals. These switches provide bidirectional connections when "on" and high impedance paths when "off." There’s … [Read More...] about How to specify and use analog switches
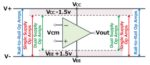
How do comparators and op amps compare?
Operational amplifiers (op amps) and comparators have two inputs, inverting and noninverting, and an output that can usually swing from rail to rail and have the same schematic symbol. So, what’s the … [Read More...] about How do comparators and op amps compare?
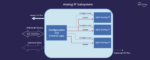
Analog subsystem simplifies integration of multiple analog IPs into ASICs
Agile Analog has launched its first range of analog subsystems, covering power management, PVT sensing, and sleep management. These innovative, digitally wrapped subsystems significantly reduce the … [Read More...] about Analog subsystem simplifies integration of multiple analog IPs into ASICs
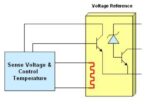
How to specify and use voltage references
Voltage references are small components that can have a significant impact, either positive or negative, on system performance. They are precision devices that maintain a constant voltage output even … [Read More...] about How to specify and use voltage references

When reality intrudes on component models and equivalent circuits
Determining the utility of an equivalent-circuit model versus construction reality is often a difficult challenge. Using simplified, first-order approximations in models and equivalent circuits is … [Read More...] about When reality intrudes on component models and equivalent circuits

Stamped spring pin socket features no solder PCB mount
Ironwood Electronics introduces stamped spring pin socket addressing high performance requirements for testing BGA35 - CBT-BGA-7525. The contactor is a stamped spring pin with 8 gram actuation force … [Read More...] about Stamped spring pin socket features no solder PCB mount

Specialty compound addresses stringed demands of BiTS used to stress test
SABIC introduced the LNP KONDUIT 8TF36E compound, a new specialty material that helps address the stringent demands of burn-in test sockets (BiTS) used to stress-test double-data-rate (DDR) memory … [Read More...] about Specialty compound addresses stringed demands of BiTS used to stress test