The terahertz part of the electromagnetic spectrum between millimeter waves and optical range remains a largely untapped, difficult-to-use resource; researchers are investigating different techniques for efficiently generating terahertz waves to promote use of this part of the spectrum.
Approach #2: Infrared Lasers and Plasma
A research group based at TU Wein (Vienna University of Technology), in close cooperation with a team from the Institute of Electronic Structure and Laser (IESL) Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas (FORTH) in Heraklion, Greece, and some help from Texas A&M University at Qatar has developed a source which is both fairly efficient and can generate waves across the entire terahertz span of spectrum. The results of the experiment, which is claimed to have broken previous records in these areas, was inspired by a theory developed in Texas A&M University which predicted that long-wavelength laser pulses could be used to achieve extremely efficient terahertz generation in air plasma.
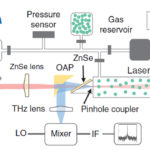
In the set-up schematic (Figure 1), the generation of the terahertz waves begins by sending infrared laser light through a nonlinear medium where part of the infrared radiation is transformed into optical radiation at twice the initial frequency. The two radiation waves are then superimposed, which creates an electromagnetic wave with an electric field having a very specific asymmetric shape.
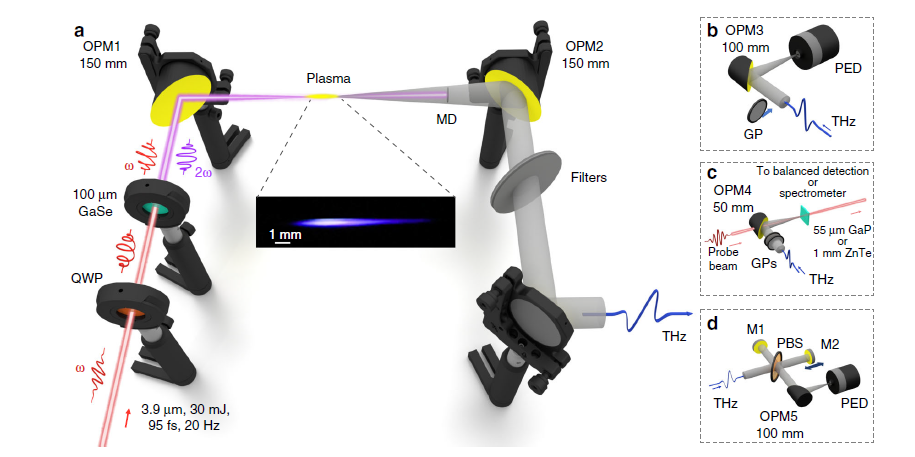
But that’s only the start of this process. The intense wave “rips” electrons out of the molecules in the air, turning the air into a glowing plasma, and the special shape of the wave’s electric field accelerates the electrons in such a way that they produce the desired terahertz radiation. As noted by team member Claudia Gollner “Our method is extremely efficient with 2.3% of the supplied energy converted into terahertz radiation. That is orders of magnitude more than can be achieved with other methods. This results in exceptionally high terahertz energies of almost 200 microjoules and terahertz-field amplitudes exceeding 100 MV per cm.”
The details including a review of existing methods of terahertz generation and their characteristics are in their paper “Observation of extremely efficient terahertz generation from mid-infrared two-color laser filaments” published in Nature Communications, along with even-more detailed, equation-laced Supplementary Information.
Terahertz Perspectives
IEEE Spectrum, “Wireless Industry’s Newest Gambit: Terahertz Communication Bands”
IEEE Spectrum, “Terahertz Waves Could Push 5G to 6G”
IEEE Spectrum, “The Truth About Terahertz”
EE World Online References
Terahertz Laser Pulses Amplify Optical Phonons in Solids
Terahertz Technology Creates New Insight Into How Semiconductor Lasers Work
Scientists Fine-Tune Carbon Nanotubes For Flexible, Fingertip-Wearable Terahertz Imagers
The Future Of Wireless Communications Is Terahertz
Bridging The Terahertz Gap
Inspecting Matter Using Terahertz Light
Graphene And Terahertz Waves Could Lead The Way To Future Communication
Wave of the Future: Terahertz Chips a New Way of Seeing Through Matter
Terahertz Wireless Could Make Spaceborne Satellite Links as Fast as Fiber-Optic Links
NUS Engineers Develop Low-Cost, Flexible Terahertz Radiation Source for Fast, Non-Invasive Screening
Researchers Whip Up Terahertz Radiation at Room TemperatureZ
Light-powered 3-D Printer Creates Terahertz Lens