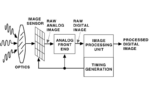
Most electronic systems rely on regulators to deliver stable direct current (DC) levels. This article explains how regulators operate and reviews the two primary types of regulators used for DC-to-DC conversion: switching and linear. It also compares their advantages and limitations, highlighting common use cases and applications for each. Regulating and refining DC voltage levels […]
Featured
Passive RFID finds unanticipated mass-market applications: part 2
Passive RFID tags have been widely adopted, and some applications show creative adaptation to unmet needs. While many uses for passive RFID tags were predicted and expected, innovators implemented some that were not obvious. This part will look at two of those applications. Clothing-store “mass” checkout One obvious application predicted for passive RFID labels was […]
Passive RFID finds unanticipated mass-market applications: part 1
Passive RFID tags have been widely adopted, and some applications show creative adaptation to unmet needs. It’s interesting to see how advances in technology often are adapted to applications that were not highlighted in their original “use case” scenarios and how clever people adapt or leverage new technologies in unscripted ways. A good example of […]
What are the different types of circuit simulation?
Electronic engineers use advanced simulation tools to create virtual representations of complex electronic circuits. These “digital twins” streamline the circuit design process, accurately modeling silicon behavior and performance before physical fabrication. This article reviews the three primary circuit simulation categories: analog, digital, and mixed. It also discusses different simulation levels, such as block and chip, and […]
What is analog design for integrated circuits?
Analog design for integrated circuits (ICs) involves creating devices and systems that process continuous signals. Analog plays a crucial role in translating real-world information such as sound, light, and temperature into electrical signals and vice versa. This article discusses the primary differences between analog and digital ICs, reviews key analog applications, and explores common analog […]
If you’re designing RFICs, here are some tools to consider
Radiofrequency ICs (RFICs) are found in consumer devices, portable electronics, automotive, military, and medical systems. They typically operate from several hundred MHz to multiple GHz. Those high frequencies present designers with significant layout challenges to ensure proper functioning, including the use of transmission line technology for efficient operation. This FAQ presents several options for RFIC […]
If you’re designing mixed-signal ICs, here are some tools to consider
Mixed-signal ICs are increasingly common in automotive, internet of Things (IoT), medical, industrial, consumer, and other applications. Designing mixed-signal ICs is more complex than simply designing an analog section and a digital section. There’s the interactions and interconnections between the sections, and the need to integrate software into the final solution. That makes designing mixed-signal […]
If you’re designing MEMS devices, here are some tools to consider
The uses for microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) devices have grown exponentially. Applications for MEMS technology include actuators, sensors, inertial measurement units (IMUs), energy harvesters, pumps, motors, oscillators, resonators, and more. They are used in all areas, from consumer to medical, military, and space. Two keys to the expansive uses of MEMS devices include the ability to […]
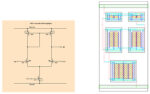
What are the elements of analog IC EDA tools?
Analog functions like sensor interfaces, signal conditioning, power management, and energy harvesting are needed in many applications. These functions are implemented with circuits like operational amplifiers, regulators, filters, sense amplifiers, low-noise amplifiers, phase-locked loops, analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), mixers, analog receiver front ends, and so on. These functions complement digital processing and can be implemented as […]
If you’re designing analog ICs, here are some tools to consider
Designing analog ICs can be a time-consuming and nit-picky process. As with the design of digital ICs, speed, power, and area (SPA) considerations are important. However, in the case of analog ICs, added challenges include gain, bandwidth, signal distortion, noise sensitivity, power supply sensitivity, thermal sensitivity, and more. All the major electronic design automation (EDA) […]