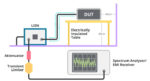
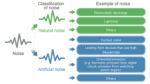
In addition to the International Telecommunications Union (discussed in part 1 of this FAQ series), there are several organizations that define and regulate acceptable levels of conducted and radiated emissions from electronic devices. These various agencies have developed numerous standards generally based on the operational environment of the specific device. Effectively managing EMI is a […]
EMI, EMC, EMS, and the ITU
Controlling electromagnetic interference (EMI), also referred to as radio frequency interference (RFI), and minimizing electromagnetic susceptibility (EMS) are two important aspects of maintaining electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). Ensuring electromagnetic compatibility at a specified level and under specific operating conditions is a common demand in the design of almost all electronic systems. Common terms used when discussing […]
Sound design considerations for Class D amps
The first two FAQs in this series, “Class D Amplifiers for High-Efficiency Switched-Mode Sound” and “Class D Audio – Why Now?” focused on basic Class D amplifier topologies, modulation techniques, general component and technology advancements that have made Class D amplifiers an increasingly viable option, and the evolving tradeoffs between silicon and GaN power devices. […]
Class D audio – Why now?
Class D amplifiers were first proposed in the 1950s. Why have they only recently been gaining more widespread popularity? The answer involves several factors: There were no switching transistors that met the performance demands of Class D amplifiers until the 1980s. And it was not until the mid-1990s that Class D integrated circuits became available. […]
Class D amplifiers for high-efficiency switched-mode sound
Sound is an analog or linear phenomenon. Traditional audio amplifiers such as Class A and Class AB operate the amplifying transistors in the linear mode. Class A and AB amplifiers can provide clean sound, but are inefficient, like linear power supplies. Class D amplifiers are similar to switched-mode power supplies and use various pulse modulation […]