Semiconductor design complexity has increased exponentially in recent years, and this challenge is exacerbated by the need to collaborate and scale across multiple, globally distributed teams while accelerating time to market. On top of these elements, the industry has been confronted with a major obstacle: the current talent shortage. There is no quick fix to […]
Industry Experts
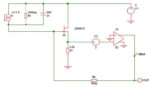
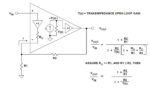
Improving transimpedance amplifiers with a bootstrap
Analog bootstrap circuits are traditionally ones where output is fed back to the input, usually to increase input impedance. This can be to minimize either the resistive or reactive (usually capacitive) components of the input impedance or both. The term is now also used with MOSFET drivers where a capacitor is charged and used to […]
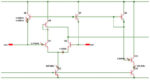
Input bias current cancellation in bipolar op amps
Bipolar operational amplifiers have an essential input bias current requirement. This bias current has to come from somewhere and can be a nuisance in some types of high impedance circuits such as charge amplifiers and transimpedance amplifiers and can result in offset voltages where input resistances aren’t matched. The example shown below has an input […]
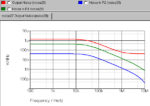
Noise simulation and analysis with SPICE
When designing low noise circuits – signal conditioning circuits, amplifiers or analog to digital converter interfaces, for example – SPICE simulation can be helpful in ensuring you have a low noise solution, particularly where signal conditioning circuits are high gain. Input referred or output noise? One decision you need to make in noise analysis is […]
Electrical noise can come from anywhere
Any unwanted signal that’s combined with the desired signal is called noise. In any circuit, noise can come from anywhere; from external systems as well as from within a circuit itself. External sources include a number of sources such as power lines, RF transmitters, nearby conductors, ignition systems, or motors that turn on and off […]
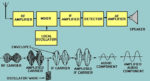
Radio receiver architectures, Part 1—TRF and Superhet
A transmitter has much-less challenging task than the receiver. The former operates on a higher-level, known signal in a known setting, while the latter must find and decode a largely unknown signal corrupted by internal and external noise, interference from other signals, distortion, low signal levels, and constantly changing parameters. This FAQ looks at the […]
RS-232 and related standards, Part 1
High-speed, high-performance “just plug and go” wired-communications interfaces such as Ethernet and USB are in wide use. In contrast, the technically ancient RS-232 standard and related standards seem like antique museum pieces with no design-in interest. However, that is a simplistic view of the reality. Although not necessarily the first choice or obvious choice in […]
IBIS model: How can it help with signal analysis?
An Input Output Buffer Information Specification (IBIS) model is a standard in the semiconductor industry for modeling semiconductor devices from a behavioral perspective, for both analog and digital perspectives. IBIS modeling enables engineers to describe detailed signal behavior in a circuit design without revealing proprietary information about the circuits (or the processes used to make […]
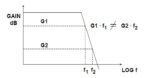
Current feedback amplifiers, Part 2
Part 1 of this FAQ look at the operation of the CFB op amp and compared it to the VFB op amp. Part 2 continues the discussion of these two op amp topologies and their characteristics. Q: How do you choose between VFB versus CFB? A: Today’s CFB and VFB amplifiers have comparable performance, but […]
Current feedback amplifiers, Part 1
Almost every engineer who has to deal with real-world signals, analog sensors, front-end circuitry, filtering, line drivers/receivers, or general amplification is familiar with the basic operational amplifier (op amp) which is the building block of most analog circuity. These op amps generally use voltage feedback (VFB), and have been studied and used extensively. However, there […]