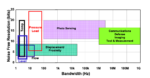
Assuming that you are familiar with the fundamental specifications of an ADC and what they mean, the next step is to know your entire signal chain well and then work to fit the ADC to the requirements. After carefully determining signal chain requirements, then select your ADC with the understanding that if the ADC is […]
basics
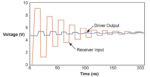
Reducing ringing or reflections by controlling impedance lines
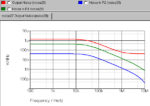
What is a controlled impedance line? For one thing, the term has to do with Printed Circuit Board (PCB) traces and layouts, which get more complex with higher frequency signals. Generally, you need not worry much about controlling impedance in traces unless you are working with signals at or above 50 MHz. However, most of […]
Improving transimpedance amplifiers with a bootstrap
Analog bootstrap circuits are traditionally ones where output is fed back to the input, usually to increase input impedance. This can be to minimize either the resistive or reactive (usually capacitive) components of the input impedance or both. The term is now also used with MOSFET drivers where a capacitor is charged and used to […]
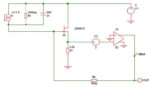
Input bias current cancellation in bipolar op amps
Bipolar operational amplifiers have an essential input bias current requirement. This bias current has to come from somewhere and can be a nuisance in some types of high impedance circuits such as charge amplifiers and transimpedance amplifiers and can result in offset voltages where input resistances aren’t matched. The example shown below has an input […]
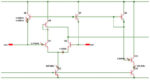
Noise simulation and analysis with SPICE
When designing low noise circuits – signal conditioning circuits, amplifiers or analog to digital converter interfaces, for example – SPICE simulation can be helpful in ensuring you have a low noise solution, particularly where signal conditioning circuits are high gain. Input referred or output noise? One decision you need to make in noise analysis is […]
Electrical noise can come from anywhere
Any unwanted signal that’s combined with the desired signal is called noise. In any circuit, noise can come from anywhere; from external systems as well as from within a circuit itself. External sources include a number of sources such as power lines, RF transmitters, nearby conductors, ignition systems, or motors that turn on and off […]
Step-by-step PCB soldering tips for newbies
The traditional, older type of solder is a mixture of lead (Pb) and tin (Sn). This type of (60/40 – Pb/Sn) solder melts at 200°C and is typically made up of 60 percent tin and 40 percent lead. However, lead-free solder is desirable today, in terms of avoiding a toxic environment. Lead-free solder is a […]
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Part 1: how it works
The modern MRI system is an amazing blend of diverse technologies, based on the realization that a small but critical aspect of the spin of hydrogen nuclei could be leveraged to provide a safe, non-invasive way to see inside a human body. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an extraordinarily valuable and vital tool for non-invasive […]
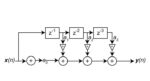
Filters, Part 1: Analog, switched, and digital filters
Filters are essential functions in most circuits and systems; as frequencies extend into the multi-GHz range, surface acoustic wave (SAW) and bulk acoustic wave (BAW) filters are needed to meet the design objectives. An engineer I worked with (and whose name I have forgotten) once remarked to about electronic filters (and he was serious): “like […]
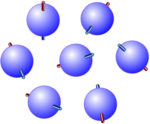
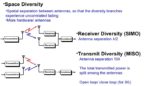
Signal-channel diversity and fading, Part 1: Space diversity
In the engineering context, the phrase “channel diversity” refers to various techniques for getting a signal from point A to point B. The different approaches to diversity can be used individually or in combination. Q: What are the primary types of channel diversity in use? A: There are two primary types: space (spatial), and frequency. […]