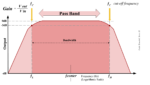
Filters will allow some signals to pass through while blocking others. A bandpass (a.k.a. band-pass) filter allows signals of a certain frequency range (“a band of frequencies”) to pass through the filter as-is. (This range of accepted frequencies is called the passband. The size or range of the passband is called the bandwidth.) With a […]
FAQ
Making sense of thermocouples and interfaces, part 2
Part 1 of this FAQ looked at the basics of thermocouples, where and why they are used, and some basic implementation issues; this part explores interface issues, cold junction compensation, and linearization. What are the requirements for thermocouple interface electronics? The thermocouple voltage is relatively small, so long leads between the thermocouple and the electronic front-end […]
Unity gain amplifier or voltage follower in a voltage divider
A voltage follower is also known as a unity gain amplifier, a voltage buffer, or an isolation amplifier. In a voltage follower circuit, the output voltage is equal to the input voltage; thus, it has a gain of one (unity) and does not amplify the incoming signal. The voltage follower does not need any external […]
Passive sensors and active sensors: What are they?
“Passives” in general within the electronics community are devices that do not drive or transmit power or signals. Passive Sensors do not control electricity directly and do not require external power sources to accomplish control of an electrical signal. Examples of passive components are resistors (R), capacitors (C), inductors (L), transformers, antennas, potentiometers (variable resistors), […]
Mutual inductance & transformers: when EMF becomes EMI
Mutual inductance is superbly demonstrated in a transformer. Transformers are made up of two wire coils placed close each other such that current running in one coil can induce a voltage in the other coil without the coils touching. Power can be transferred without a metal connection with a transformer, and transformers can be […]
Phase Locked Loop: A fundamental building block in wireless technology
A phase-lock(ed) loop (PLL) is a fundamental building block in wireless, radio frequency (RF), and telecommunication technologies. PLLs use a negative feedback circuit to match the phase of the frequency of another signal. PLLs synchronize the phase of the PLL’s output to the input signal’s frequency by tweaking the output of a voltage-driven oscillator; the […]
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): what is it and how does it work?
Digital signals have two positions: on or off, interpreted in shorthand as 1 or 0. Analog signals, on the other hand, can be on, off, half-way, two-thirds the way to on, and an infinite number of positions between 0 and 1 either approaching 1 or descending down to zero. The two are handled very differently […]
What is a clock and what are its critical parameters (Part 2)?
The performance of a clock function, which includes the crystal and associated circuitry, is defined by parameters which are measured over both the short term and long term. It is also characterized by change in specifications due to temperature variations, aging, and mechanical considerations such as vibration and shock. How is clock performance defined? Both […]
What is a clock and what are its critical parameters (Part 1)?
The “clock” function is a standard part of nearly every electronic system, with very few exceptions. Behind this simple-sounding, commonplace word, there is an array of complexity and subtlety in definition, performance, and design. Clocks are both vital and ubiquitous, so it is worth understanding the different functions they fulfill, they ways they can be […]
How should grounds and commons be connected to each other?
We have already looked briefly at Earth ground (if any), chassis ground, and commons (often misnamed as “grounds”). These do not exist as unrelated connections in a system. The issues related to connecting commons and ground is the subject of countless articles, academic papers, vendor application notes, anecdotes, and even books. There are many rules […]