We went into our article archives to uncover the most widely read posts on analogictips.com over the past 12 months. Here for your reading (or re-reading?) pleasure are the top 10 stories: How IoT and mixed signal designs will drive SiP tech in 2016 How much math do you need to know to design electronics? […]
FAQ
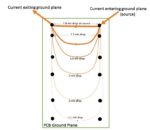
What is common-impedance coupling?
Common-impedance coupling occurs when two or more circuits share a common ground and is the result of a shared impedance in a shared ground path. The best way to explain it is by way of a common example, such as when the lights dim when an air conditioner is turned on; they probably share the […]
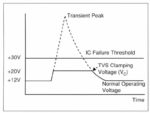
Transient Voltage Suppressor Diode: What is it?
Transients are sudden high-frequency overvoltages that can destroy a chip. A silicon Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS) is a circuit protection component that either attenuates (reduces) or filters a transient voltage spike (overvoltage), thus protecting your circuit. Another type of TVS diverts a voltage spike away from your circuit (also known as shunting, clamping, or bypassing.) […]
Supercapacitor or ultracapacitor basics: What you need to know
A supercapacitor, also known as an ultracapacitor, is a high-capacity capacitor that possesses a lower energy density than batteries, but higher than conventional capacitors. In the race for longer smartphone life, batteries have not made as much progress in the capacity as semiconductors have made in power efficiency. However, semiconductors are fast approaching a point […]
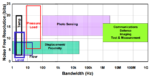
Trade-offs in reducing noise with linear power supplies vs. switch mode power supplies
Some analog applications are very noise sensitive such as medical equipment, communications equipment, instrumentation, or test and measurement equipment. Elimination of all potential noise sources in a circuit may be necessary, including conducted, radiated, and thermal noise. One possible source of conducted noise can be found in the power supply bus. Eliminating this noise […]
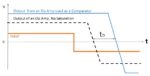
Should I use an op amp as a comparator?
Perhaps you have a quad pack of op amps, are using only three, and need a single comparator. It might be tempting to use the remaining op amp as a comparator, after all, both have high gain, low offset, and high common-mode rejection. But it’s easier said than done, because a comparator and an op […]
Why do industrial sensors measure in 4-20mA to programmable logic controllers?
A large number of sensors that take in and translate data from the real world into electrical signals are analog sensors, and if listed as digital sensors, it’s because they have integrated analog-to-digital converters. Traditionally, wired sensors have altered an electrical current in response to environmental conditions. Sensors range from familiar examples like photodiodes and […]
General tips for preventing problems in analog circuits
Tips for preventing problems could fill a book, especially if every professor, technician, or engineer were to contribute tricks and tips that they have learned over the years. However, many will agree that an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. Here, we present a few general tips that may seem obvious to […]
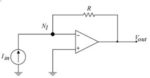
Transimpedance amplifier role in current to voltage conversion
A transimpedance amplifier (TIA) converts current to voltage. Transimpedance amplifiers can be used to process the current output of photodiodes, pressure transducers, accelerometers, and other types of sensors to a voltage formatted as a useable signal output. TIAs provide simple linear signal processing using an operational amplifier and a resistor for dissipating current. Figure 1 […]
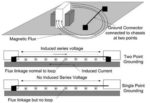
Ground rules: earth, chassis, and signal ground
In analog design, the relationship of a signal to ground is of fundamental concern (and can create issues in digital designs, too.) However, “ground” as a concept can be confusing as it relates to three different situations: chassis ground, signal ground, or earth ground. All three indicate connecting to a point of (theoretically) zero voltage, […]